|
CA06-005
|

|
The bizarre floral appearance of Hydnora africana seems almost extraterrestrial,
but in fact it is finely adapted for pollination in its arid habitat. This
plant, resident of southern Africa only emerges from the soil to flower.
After the fleshy petals open, the flower begins to emit an odor of rotting
meat to attract its pollinators, carrion flies and beetles. The unusual
underground habit and lack of leaves may be explained by its mode of nutrition.
Hydnora africana is a root holoparasite. Thus it has no need for
sunlight to generate sugars, it has no chlorophyll and attains all nutrients
and water from the roots of its shrubby host plant (in the background) Euphorbia
mauritanica.
|
copyright: -
license: - |
Image
|
Conant Award

|

|
|
CA06-006
|
|
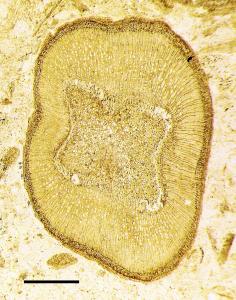
Cross section of a twig from a woody flowering plant that lived during the Eocene epoch, approximately 40 million years ago. The specimen is anatomically preserved by silica mineralization in rocks known as the Clarno Chert. All tissues are preserved, from the central pith to the outer bark. The plant was part of a subtropical community inhabiting marshlands in what is now central Oregon.
|
copyright: -
license: - |
Image
|
Conant Award

|

|
|
CA06-007
|
|
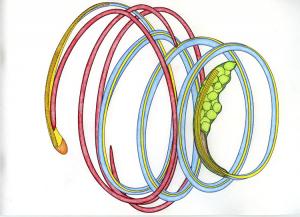
This is a three-dimensional image of a sperm cell of the liverwort, Pellia epiphylla, drawn from two-dimensional TEM images. Sperm cells are released from the male antheridia located on the thallus and swim to a receptive female egg. Upon fertilization, a zygote is formed.
|
copyright: -
license: - |
Image
|
Conant Award

|

|
|
CA06-008
|
|
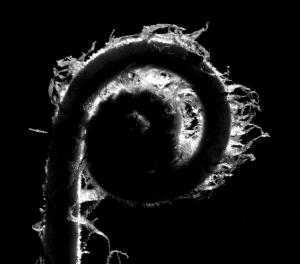
In most ferns the young leaf uncoils during development; these coiled fronds are commonly referred to as "fiddle heads". This photo shows this type of leaf development, known as circinate vernation in Thelypteris extena.
|
copyright: -
license: - |
Image
|
Conant Award

|

|
|
CA06-009
|

|
In most ferns the young leaf uncoils during development; these coiled fronds are commonly referred to as "fiddle heads". This photo shows this type of leaf development, known as circinate vernation in Thelypteris extena.
|
copyright: -
license: - |
Image
|
Conant Award

|

|
|
CA06-010
|

|
In most ferns the young leaf uncoils during development; these coiled fronds are commonly referred to as "fiddle heads". This photo shows this type of leaf development, known as circinate vernation in Thelypteris extensa.
|
copyright: -
license: - |
Image
|
Conant Award

|

|
|
CA06-011
|

|
This photograph shows the remarkably persistent leaves on the trunk of a young pehuén (also called the monkey puzzle tree), Araucaria araucana, in the central Chilean Andes. Even as the main trunk of this slow-growing conifer expands and becomes woody, the trunk leaves remain green and apparently functional. The very stiff and prickly leaves of this species are among the most long-lived of all plants, with a mean leaf lifespan estimated at 24 years (Lusk, 2001). Interestingly, the toughness of Araucaria araucana's leaves accounts for its English common name. Around 1850, an observer of a young tree being grown in Cornwall, England remarked, in reference to the tree's sharp and prickly leaves, "It would puzzle a monkey to climb that". Lusk, C. H. 2001. Leaf lifespans of some conifers of the temperate forests of South America. Revista Chilena de Historia Natural 74:711-718.
|
copyright: -
license: - |
Image
|
Conant Award

|

|
|
CA06-012
|

|
Utricularia gibba is an aquatic, carnivorous plant. Utricularia species, commonly called the Bladderworts, are found in aquatic areas throughout the United States living in bodies of water or moist environments, such as bogs. This specimen was collected in a pond in South Florida, but visitors to Everglades National Park would be able to see several Utricularia species. The traps of this plant are very small, only a few millimeters, and are easily missed unless the observer looks closely. Hundreds of traps are found along the plant body, a horizontally growing stem called a stolon. Bladderworts are the only carnivorous plant that catches prey by a suction trap. These traps actively expel water from the inside of the trap, or the trap lumen. While the traps excrete water, the trap sides are sucked in and the trap walls appear concave. Once the trap is set, it is ready to catch prey. Small organisms, such as rotifers, copepods and mosquito larvae, swimming in the water or grazing on Utricularia, may accidentally hit the trigger hairs, appendages at the front of the trap, and cause the trap door to open inward. Once the trap door is open, water and the unsuspecting organism rush in with the trap door closing behind the prey. After the trap has fired, the trap walls are convex and appear more round. Although complex, the trapping process, including resetting, takes only thousands of a second. Digestion of the prey follows capture via four and two-armed hairs inside the trap lumen. Carnivorous plants, including Utricularia species, are usually found in nutrient poor sites and their ability to trap and digest prey allows them to supplement available nutrients and survive in nutrient poor habitats.
|
copyright: -
license: - |
Image
|
Conant Award

|

|
|
CA06-013
|
|
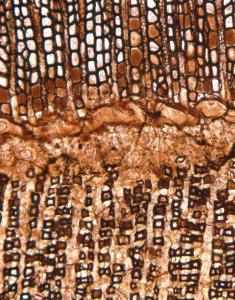
Cycadeoidea (Bennettitales) is an extinct genus of seed plants that thrived in the Cretaceous (100 million years ago). This specimen was collected from the Black Hills of South Dakota. At the bottom of the picture is secondary xylem (wood) represented by the dark colored cells. At the top of the image is secondary phloem. Phloem is rarely preserved in the fossil record and the excellent preservation seen here is vital to studies on vascular tissue in fossil plants. (specimen from Yale University Peabody Museum of Natural History)
|
copyright: -
license: - |
Image
|
Conant Award

|

|
|
CA06-014
|

|
Stomata regulate gas exchange and are interspersed among flat tightly packed epidermal cells. This colorized scanning electron micrograph shows the sunken stoma of Equisetum arvense with the guard cells nearly hidden by overlying subsidiary cells. Highlighted in grey is the silica found in the epidermis, which gives Equisetum arvense a rough feel and the common name scouring rush.
|
copyright: -
license: - |
Image
|
Conant Award

|

|
|
CA06-015
|

|
Dioon spinulosum is a gymnosperm that links ancient plants to today. With an explosion in the Mesozoic era, in concert with dinosaur diversification, this era is often referred to as the "Age of Cycads and Dinosaurs". The leaves of cycads occur in a cluster at the top of the stem and resemble palms. Unlike palms, cycads exhibit true secondary growth from a vascular cambium.
|
copyright: -
license: - |
Image
|
Conant Award

|

|
|
CA06-016
|
|
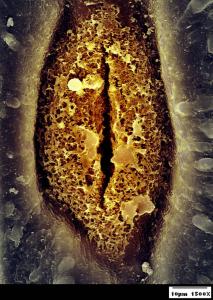
Stomata regulate gas exchange and are interspersed among flat tightly packed epidermal cells. This scanning electron micrograph was colorized to emphasize the sunken stoma of Psilotum nudum, commonly known as the whisk fern. Epicuticular wax is formed as webbing over the gaurd cells.
|
copyright: -
license: - |
Image
|
Conant Award

|

|
|
CA06-017
|
|
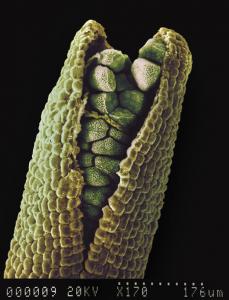
This picture is of a hornwort sporophyte, one of the earliest lineages of land plants. The hornworts are interesting because of many unique features. The sporophyte is the result of fertilization. Hornworts have cone or horn shaped sporophytes. The sporophyte produces haploid spores that grow into new plants. In most hornworts, the spores are a single cell. However, in Dendroceros the spores are multicellular. Most hornworts grow on exposed soil in wet areas. Dendroceros is extremely interesting because it is the only hornwort that grow on trees.
|
copyright: -
license: - |
Image
|
Conant Award

|

|
|
ca07-012
|

|
The Algodones Dunes of southeastern California and northeastern
Baja California can be quite an inhospitable place. Temperatures
in the summer seldom drop below 105 degrees Fahrenheit, rain
is a scant 2 inches per year on average, and active sand creates
challenges for even the most versatile of organisms. Many
highly specialized plant species have become adapted to life
on the Algodones Dunes. Termed endemic species, these plants
are found nowhere else in the world. Most peculiar of the
Algodones Dunes endemic species is Pholisma sonorae,
commonly known as sandfood. P. sonorae is a holorhizoparasite,
meaning that it invades and persists within the root system
of host plants such as Tiquilia plicata and Eriogonum
deserticola, from which it steals essential sugars without
providing any benefit to the host. During the flowering period
of P. sonorae, it develops a fleshy-stemmed shoot
that pushes upward through the sand, eventually terminating
in a "mushroom-shaped" inflorescence at the surface.
The inflorescence, shown in this picture, is quite impressive
to behold. It is even more impressive when one considers that
the host roots are often up to 6 feet below the surface of
the dunes!
|
copyright: 7-1-2005, Summer, BSA
license: - |
Image
|
Conant Award

|

|
|
ca07-029
|
|
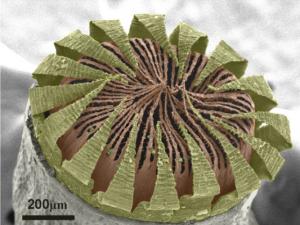
The peristome is located around (peri-) the mouth (-stome) of the moss capsule, a structure which contains the spores. For the past 200 years, peristome characteristics have played an important role in defining major groups of mosses. The peristome shown here has a unique morphology and is an identifying feature for the Timmiaceae. This scanning electron micrograph of Timmia megapolitana has been colored to highlight the two layers of the peristome. The endostome (inner layer, colored in orange) consists of a membrane that is topped by 64 filaments, while the exostome (outer layer, colored in yellow) consists of 16 large teeth. These teeth have the ability to move in response to humidity, thus opening and closing the mouth of the moss capsule. This movement facilitates the release of spores (colored in green) under optimal dispersal conditions.
|
copyright: Budke, BSA
license: http://images.botany.org/index.html#license |
Image
|
Conant Award

|

|
|
ca07-038
|

|
One of the most conspicuous developmental changes observed in juvenile leaves as they mature is color change, with young leaves on new growth tips of many species first appearing red, purple, pink, or less commonly blue or white, and becoming greener with leaf age. The red-to-blue coloration of young leaves is most commonly due to the pigment anthocyanin, appearing within vacuoles of epidermal and/or mesophyll cells within hours to days of seedling germination, and then decreasing concomitantly with leaf expansion and maturation. The functional significance of this pigment in juvenile leaves still remains largely unresolved, as mixed support has been shown for it acting as a camouflage against herbivory, a fungicide, a signal indicating the presence of unpalatable phenolics, and also an antioxidant. Perhaps the most compelling current explanation is that the pigment act as a light-attenuating molecule (the plant-equivalent of sunscreen), protecting underlying cells from high irradiance through absorption of high energy blue-green (and possibly UV) wavelengths of the solar spectrum. Because immature leaves tend to be especially vulnerable to high-light stress due to immature chloroplast structure, reduced capacity of photosynthetic enzymes, and limited stomatal and cellular conductance of CO2, young leaves growing under high irradiances tend to photosynthetically saturate, as well as photoinhibit, under substantially lower sunlight levels than mature leaves. It is therefore generally beneficial for light capture to be down-regulated early in leaf development, until light-processing and carbon-fixation processes have matured to adequately balance energy capture with utilization. Ailanthus altissima represents one of many early successional species that exhibit anthocyanin in developing leaves.
|
copyright: Hughes, BSA
license: http://images.botany.org/index.html#license |
Image
|
Conant Award

|

|
|
CA08-003
|

|
The Hawaiian violets are monophyletic lineage of angiosperms that have undergone a putative adaptive radiation throughout the Hawaiian Islands. Species in similar habitat types (cloud forest, high-elevation bog, and mesic streambank) exhibit remarkable parallelisms in leaf morphology and growth form. Viola robusta was formerly classified as a subspecies of Viola chamissoniana, a dry cliff violet restricted to O'ahu. Recent molecular systematic investigations of the Hawaiian violet lineage suggests that Viola robusta is not a subspecies of Viola chamissoniana.
|
copyright: Havran, BSA
license: http://images.botany.org/index.html#license |
Image
|
Conant Award

|

|
|
CA08-004
|

|
The plant is commonly distributed in north China and the blooming season is around early summer, and it's different flower architecture makes it very different with others in the garden.
|
copyright: Qing, BSA
license: http://images.botany.org/index.html#license |
Image
|
Conant Award

|

|
|
CA08-005
|

|
This nice and beautiful camellia was very popular for most Chinese due to a famous chinese sowardmem film. Also the camellia is famous and popular for it's nice flower and smell and its different blooming season around the new year.
|
copyright: Qing, BSA
license: http://images.botany.org/index.html#license |
Image
|
Conant Award

|

|
|
CA08-006
|

|
This glamorous waterlily catched most our interesting during it's blooming in cold winter when it's snowing outside in North China.
|
copyright: Qing, BSA
license: http://images.botany.org/index.html#license |
Image
|
Conant Award

|

|